The Key to Pharmaceutical Automation Success
The success of pharmaceutical automation relies on adherence to the strictest regulations, such as the cGMP, or the Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). These requirements include a number of other factors, including the adherence to the governing body of the FDA. For example, 21 CFR Part 11 compliance requires companies to submit validation documents to the FDA, which contain a series of tests to validate systems and software. Additionally, adherence to the requirements for the use of digital signatures means companies must implement written policies that place responsibility on the signer. Further, the regulations also require companies to provide FDA with copies of their complete records.
Pharmaceutical Automation
The key to Pharmaceutical automation success lies in the adherence to the strict regulatory requirements of CFR Part II, including the GAMP Guide. This guide provides guidance for implementing quality assurance systems. The GAMP Guide describes a methodology for the production of quality equipment using a life cycle model and concept of prospective validation. It is a set of guidelines designed to help pharmaceutical organizations better understand FDA regulations. GAMP-5 establishes common language and standards for system life cycle approaches.
The adherence to 21 CFR Part 11 is not new. This document was first issued 22 years ago and continues to evolve with advances in technology. Compliance efforts in the Life Sciences industry are more important than ever. With a growing reliance on computerized systems and the lack of resources, organizations must understand the scope of applicable regulations and focus their compliance efforts accordingly. To help ensure compliance, organizations must first understand the scope of the regulations, especially in the context of compliance.
In addition to these requirements, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 provides guidance on electronic records and electronic signatures. Understanding the guidance is key for developing an appropriate validation strategy. Moreover, it helps ensure the integrity of systems throughout their life cycles. ER/ES capabilities vary by case, so companies should assess the risks of not meeting the guidance. For example, some companies are not able to fully implement 21 CFR Part 11 requirements.
Industrial Automation in Pharmacetuicals
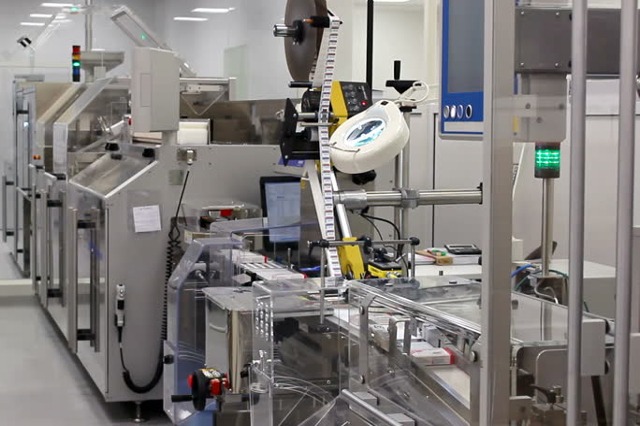
As the pharmaceutical industry faces the challenge of ever-increasing costs and a dwindling return on its research and development efforts, it has chosen to invest in industrial automation and plant automation and drive business reform through digitalization. Adherence to the stringent requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is essential to pharmaceutical manufacturing. Industrial automation and control has been a key focus in the pharmaceutical industry since the 1990s. It helps pharmaceutical manufacturers link huge amounts of information coming from multiple locations and equipment. It also helps them adhere to FDA regulations by providing different production management solutions.
The use of industrial automation and control in the pharmaceutical industry has several benefits. These include reduced resource costs, improved turnaround time, and lower reliance on full-time employee resources. Additionally, these solutions reduce the risks associated with compliance. The discovery and development of a new pharmaceutical requires several complex stages. Depending on the drug, the entire process can take 12-15 years. The price tag for the research and development phase ranges between $0.9 billion and $2 billion. And yet, despite its importance, the rate of commercialization is low.
The success of industrial automation and control in the pharmaceutical industry lies in the adherence to the FDA’s CFR Part II guideline. This guideline was created to make sure that pharmaceutical manufacturers follow the regulations and meet the safety and efficacy requirements of the FDA and European Union (EU)’s Good Manufacturing Practices. Although the guideline does not require the use of plant automation in the pharmaceutical industry, it is highly recommended.
Uptime Automation LLC
Uptime Automation LLC is a provider of automated systems for the pharmaceutical, life sciences, and food industries. They have over 10 years of experience supporting clients with FDA-regulated automation systems and have extensive knowledge of the applicable standards and documentation. For example, they understand the importance of the adherence to CFR Part II for pharma automation systems. That’s why the company partners with a variety of recognized bodies.
With the adherence to FDA regulations, pharmaceutical manufacturers are looking for ways to optimize their processes and improve production efficiency. In order to do so, they must implement advanced automation and robotic solutions. The best solutions will eliminate the need for manual data entry. This will help pharmaceutical manufacturers meet the stringent requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).